Bandages are essential tools for wound care, protecting injuries and supporting healing in everyday life. Whether you’re reaching for adhesive bandages after a minor cut or stocking bulk bandages for your first aid kits, choosing the right bandage supplies is crucial for comfort, safety, and infection prevention. In this article, you’ll discover the differences between popular bandage types, learn key techniques for bandaging, and find out which materials and features best suit sensitive skin, sports injuries, and eco-friendly needs. Get ready for expert insights and practical tips to simplify your wound care routine.
Featured Products
Best Overall • Best Value • Premium Option
Note: As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. Some of the links on this site are affiliate links — when you buy through those links, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Understanding Bandages, Gauze, Adhesion, and Wound Protection
Bandages protect wounds by covering and cushioning injuries. Gauze bandages absorb moisture and keep wounds clean. Adhesive bandages stick to the skin and seal out dirt. These wound care essentials help prevent infection and promote safe healing for everyday cuts or scrapes.
Choosing the right bandage variation depends on injury type and location. Gauze, elastic bandages, and adhesive bandages each serve different needs. Entities like wound, fabric, and residue matter for comfort and healing. Next, learn about the key features of modern wound protection supplies.
Key features of modern wound protection supplies
- Sterile bandages use non stick materials to prevent residue and reduce infection risk.
- Elastic bandages offer adjustable compression and support for different injury types.
- Waterproof bandages protect wounds during bathing or exposure to moisture.
- Modern wound care bandages often include cotton layers for comfort and breathability.
Comparing Fabric, Elastic, Sterile Bandages, and Care Techniques
Bandages come in various forms, like fabric bandages, elastic bandages, and sterile bandages. Each bandage type supports different care needs. Picking the right bandage supplies helps protect wounds and aids healing. Proper bandaging keeps injuries clean and reduces infection risk.
Fabric bandages work well for flexible areas. Elastic bandages help with sprains and swelling. Sterile bandages are vital for open wounds. Prices typically range from $3–$8 per box, depending on bandage variation. Next, explore the Pros and cons of common bandage types for better first aid decisions.
Pros and cons of common bandage types
- Elastic bandages offer strong compression but can cause circulation issues if wrapped too tightly around an injury.
- Gauze bandages absorb wound exudate well but need medical tape or a band to stay secure in first aid kits.
- Waterproof bandages keep wounds clean during bathing but may leave sticky residue on sensitive skin.
- Sterile bandages reduce infection risk for wound care but are usually single-use and not ideal for bulk bandages needs.
Selecting Wound Bandages for Cuts, Infection, and Comfort
Choosing the right bandages helps protect cuts, prevent infection, and improve comfort. Adhesive bandages seal out dirt. Gauze bandages absorb fluids and cushion wounds. These medical bandages are essential for wound care in home first aid kits.
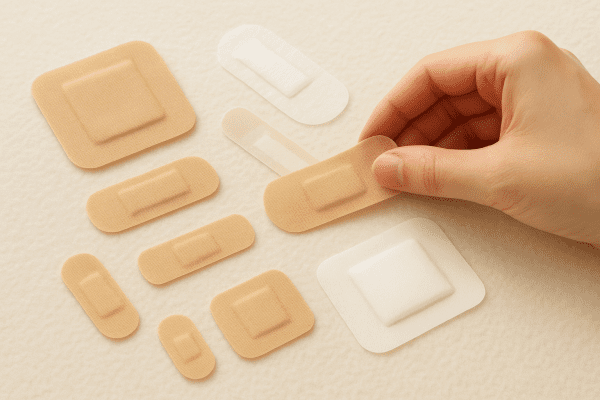

Different injuries need different bandage types. Fabric bandages flex with movement and suit joints. Sterile bandages lower infection risk for open wounds. Prices for bandage supplies typically range from $3–$8 per box. Next, see the key Factors influencing bandage choice for different injuries.
Factors influencing bandage choice for different injuries
- Moisture levels and risk of infection determine if gauze bandages or waterproof bandages are best for wound care.
- Sensitive skin may require hypoallergenic or non stick bandages for greater comfort and reduced residue.
- Location of injury, such as joints or fingers, often needs flexible fabric bandages or tubular bandage variations for secure coverage.
- Compression bandages are selected to control swelling or support injuries from sports or active use.
Bandage Materials, Absorption, Residue, and Sensitive Skin
Bandage materials affect comfort, absorption, and skin reactions. Gauze bandages offer strong fluid absorption. Some adhesive bandages can leave sticky residue on the skin. Sensitive skin may react to certain bandage types or adhesives. Choosing the right material is important for wound protection.
Non stick bandages help reduce residue and irritation. Cotton bandages allow better breathability for wounds. Self adhesive bandages vary in how much they absorb moisture. Pricing for these bandage supplies typically ranges from $3–$8 per box. Next, consider material selection for sensitive or allergy-prone skin.
Material selection for sensitive or allergy-prone skin
- Non stick bandages and cotton bandages are gentle options that reduce irritation on sensitive skin.
- Hypoallergenic adhesive bandages help prevent allergic reactions for those with skin sensitivities.
- Sterile bandages with minimal residue are ideal for wound care in allergy-prone individuals.
- Self adhesive bandages without latex protect against common bandage allergies and support comfort.
Waterproof Bandages, Cotton Layers, and First Aid Performance
Waterproof bandages shield wounds from moisture, helping prevent infection. Cotton layers in bandage types add comfort and absorb fluid. These first aid bandages protect injuries during daily routines. Proper bandaging keeps wounds clean and helps support healing in various first aid kits.
Many self adhesive bandages use cotton for softness and absorption. Waterproof bandage variations suit swimming or showering. Pricing for these wound bandages typically ranges from $3–$8 per box. Choosing the best bandage supplies depends on your needs. Next, see the effectiveness of waterproof and multi-layer bandages.
Effectiveness of waterproof and multi-layer bandages
- Waterproof bandages keep wounds dry and help reduce infection risk during water exposure.
- Multi-layer wound bandages improve absorption and cushion injuries for better first aid bandage performance.
- Self adhesive bandages with cotton layers offer comfort while maintaining strong protection for cuts and scrapes.
- Sterile bandages with moisture barriers are effective for wound care in active or outdoor settings.
Compression Bandages, Swelling, Injury, and Recovery Support
Compression bandages help manage swelling after an injury. These elastic bandages provide support and limit movement. They are a key part of recovery for sprains or strains. Proper bandaging can protect the wound and help reduce pain during healing.
Elastic bandages are used for sports injuries and swollen joints. They keep swelling down and support muscles. Gauze can be added for extra comfort. Prices for compression bandages typically range from $3–$8 per roll. Next, discover compression wrap benefits in injury management and healing.
Compression wrap benefits in injury management and healing
- Compression bandages help minimize swelling and stabilize the injury for faster recovery.
- Using an elastic bandage reduces fluid buildup and supports injured muscles in sports bandages applications.
- Proper bandaging with a compression wrap can decrease pain by limiting excessive movement around the wound.
- Compression bandages are essential in first aid kits for managing soft tissue injuries and providing ongoing support.
Pediatric Bandages, Adhesive Strength, Animals, and Safety
Pediatric bandages use gentle adhesives to protect young skin. Strong adhesion keeps bandages in place for active kids and pets. Animal bandage variations often feature soft, self adhesive materials for safety. Bandages for wounds must balance comfort, easy removal, and secure fit.
Adhesive bandages for children often include fun designs and hypoallergenic features. Pediatric bandages typically cost $3–$8 per box. Animal bandages avoid latex and use self adhesive wraps to prevent harm. Choosing the right bandage type is key for safety and comfort considerations for kids and pets.
Safety and comfort considerations for kids and pets
- Pediatric bandages with non stick surfaces help prevent residue and discomfort during removal from sensitive skin.
- Self adhesive bandages for animals should use soft fabric to avoid irritation and allow flexible movement.
- Choosing hypoallergenic wound bandages reduces the risk of allergic reactions in both children and pets.
- Sterile elastic bandages provide secure support for active play or pet injuries while maintaining safety and cleanliness.
Bulk Bandages, Storage Solutions, Expiration, and Accessibility
Bulk bandages are essential for well-stocked first aid kits. Storing bandage supplies correctly helps keep wound care items sterile and ready. Expiration dates matter for sterile bandages and medical bandages. Proper storage protects adhesive bandage variations from damage and keeps prices reasonable per unit.
Store bulk bandages in a dry, cool place. Use clear bins for easy access to wound bandages and gauze. Monitor expiration dates and rotate older dressing supplies forward. Accessibility matters for families and caregivers. Next, explore Best practices for storing and organizing bulk bandages for reliable first aid readiness.
Best practices for storing and organizing bulk bandages
- Group elastic bandages, gauze bandages, and adhesive bandage variations by size and injury type for quick access in first aid kits.
- Label storage bins with wound bandages, non stick bandages, and sterile bandages to simplify inventory checks.
- Store medical bandage supplies in sealed containers to protect from dust, moisture, and residue buildup.
- Place bulk bandages and cotton bandages on easy-to-reach shelves to improve accessibility for emergency situations.
Eco Friendly Bandages, Sustainability, Packaging, and Planet Impact
Eco friendly bandages help reduce waste and support a healthier planet. These bandage variations use sustainable materials and packaging. Many cotton bandages and non stick bandages now avoid plastic. Choosing sustainable wound bandages can lower the environmental impact of first aid kits.
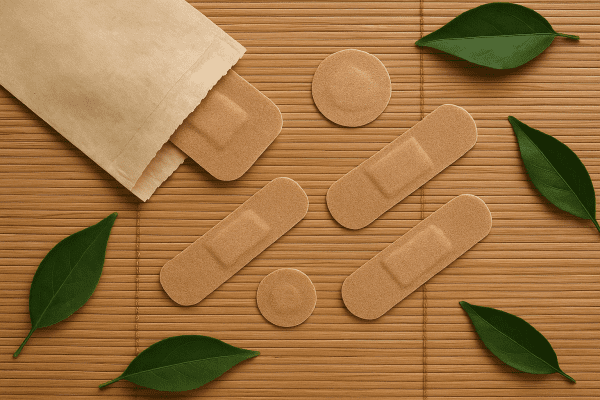

Some bulk bandages use compostable wrappers or biodegradable gauze. Packaging has shifted to recyclable boxes and less plastic residue. Prices for eco friendly bandage types are typically $4–$9 per box. Shoppers should consider sustainable bandage options and environmental considerations when restocking medical bandages.
Sustainable bandage options and environmental considerations
- Cotton bandages with biodegradable packaging help lower carbon emissions from first aid kits.
- Choosing non stick bandages with compostable wrappers reduces residue and landfill waste.
- Bulk bandages made from sustainable fabric support eco friendly wound care practices.
- Recyclable medical bandages and dressing supplies improve the planet impact of essential bandage types.
Applying Bandages, Gloves, Hygiene, and Long-Term Wound Care
Applying bandages starts with clean hands or gloves. Proper hygiene lowers infection risk for wounds. Always use sterile bandages or gauze for open injuries. Changing dressing supplies regularly keeps the wound safe. Good bandaging protects healing skin and supports long-term recovery.
Replace medical bandages if they get wet or dirty. Use non stick bandages for sensitive skin to prevent residue. Elastic bandage types help control swelling during recovery. Store bulk bandages in a clean, dry area. For best results, follow the steps for hygienic and effective long-term bandaging.
Steps for hygienic and effective long-term bandaging
- Inspect wound bandages daily for residue buildup or signs of infection.
- Rotate bulk bandages and sterile bandages to use supplies before expiration.
- Choose cotton bandages or non stick bandages for sensitive skin during extended bandaging.
- Wear gloves when changing dressing to protect both the wound and medical bandage supplies from contamination.
Final Thoughts:
Bandages are an essential part of every first aid kit, offering protection and comfort for a wide range of wounds and injuries. By understanding the differences between adhesive bandages, gauze, and other bandage types, consumers can make informed choices that suit their needs—whether for everyday cuts or specialized wound care. Remember to consider factors like sensitive skin, waterproof requirements, and proper storage of your bandage supplies. For the best results, regularly check expiration dates and restock your medical bandages to keep your home or workplace prepared for any emergency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main types of bandages and when should each be used?1
Answer: Bandages come as adhesive bandages, gauze bandages, elastic bandages, and sterile bandages. Use adhesive bandages for small cuts or wounds. Gauze bandages absorb fluids and cushion injuries. Elastic bandages help with swelling or sports injuries. Sterile bandages are best for open wounds and infection prevention in first aid kits.
How do I choose a bandage for sensitive or allergy-prone skin?2
Answer: Choose hypoallergenic bandages and non stick bandages for sensitive skin. Cotton bandages are gentle on the skin. Avoid latex in medical bandage supplies. Sterile bandages with soft fabric reduce irritation and residue. Always check bandage variation labels for allergy information. Store wound bandages in clean areas for safety.
How often should I change a bandage on a wound?3
Answer: Change wound bandages at least once daily or if wet. Replace adhesive bandages or gauze bandages when dirty. Check sterile bandages for signs of residue or infection. Keep bandage supplies clean and dry. Proper bandaging supports wound healing and infection control. Always wash hands or wear gloves before changing.
Are waterproof bandages truly effective for swimming or showering?4
Answer: Waterproof bandages protect wounds from water during bathing or swimming. Some bandage types may peel at edges. Choose self adhesive bandages with strong adhesion. Avoid using waterproof bandages on infected wounds. Cotton bandages are not waterproof. Keep bulk bandages in first aid kits for backup.
What is the difference between a bandage and a dressing?5
Answer: A bandage holds a dressing in place over a wound. Dressings are sterile pads for direct wound protection. Bandages include elastic bandages, adhesive bandages, and gauze bandages. Both are key first aid supplies. Dressing absorbs fluids; bandage secures and supports. Use both for proper wound care.
How do I apply a bandage properly to prevent infection?6
Answer: Wash hands or wear gloves before touching a wound. Use sterile bandages or gauze bandages. Cover the wound completely with a non stick bandage. Change bandage supplies if wet or dirty. Avoid touching the injured area. Proper bandaging protects wounds and reduces infection risk. Store bulk bandages safely.
Can compression bandages help with swelling or sprains?7
Answer: Compression bandages help reduce swelling in injuries and sprains. Elastic bandages provide support and limit movement. Use cotton bandages for added comfort. Ensure bandages are not wrapped too tight. Keep compression bandages in first aid kits. Change bandage supplies if dirty or loose. Proper bandaging aids recovery.
Do bandages expire and how should they be stored for best results?8
Answer: Yes, bandages and bandage supplies do expire. Store wound bandages in a cool, dry place. Keep bulk bandages sealed and away from moisture. Check expiration dates on elastic bandages, gauze bandages, and sterile bandages. Replace expired first aid bandage types for safe wound protection. Rotate stock regularly.
Last Updated on January 16, 2026 by msj484
DISCLAIMER (IMPORTANT): This information (including all text, images, audio, or other formats on FamilyHype.com) is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional advice, diagnosis, endorsement or treatment. You should not take any action or avoid taking action without consulting a qualified professional. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions about medical conditions. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking advice or treatment because of something you have read here a FamilyHype.com.


