Hydrocolloid patches have quickly become a must-have solution for anyone seeking fast, discreet relief from pimples and minor wounds. These innovative skin patches—often called acne hydrocolloid patches or gel patches—use advanced hydrocolloid dressing technology to absorb pus and protect sensitive skin from bacteria and irritation. In this article, you’ll discover how hydrocolloid products work, their benefits for acne and wound care, safety tips, and expert guidance on choosing the best patch for your needs. Ready to learn how these handy patches can transform your skincare routine?
Understanding hydrocolloid patches for acne and skin care
Hydrocolloid patches are thin, adhesive gel patches used on skin. They help protect pimples and minor wounds. These hydrocolloid dressings absorb pus and fluid while shielding skin from bacteria. Many people use hydrocolloid acne patches for fast, discreet spot treatment.
Hydrocolloid patches are popular for acne care and wound healing. They reduce picking and can minimize scarring. Many users find them helpful for whiteheads and surface pimples. Prices typically range from $6–$18 per pack. Next, explore Key features and intended uses for consumers.
Key features and intended uses for consumers
- Hydrocolloid dressings create a moist environment that supports faster skin healing and protects pimples from bacteria.
- Gel patches help absorb pus and excess fluid, making them ideal for spot treatment of zits and minor wounds.
- Adhesive patches offer a barrier to prevent touching, reducing the risk of scarring for various skin types.
- Hydrocolloid products are often used in personal care routines for both acne treatment and wound care patches on fingers or toes.
Hydrocolloid materials, adhesive layers, and fluid absorption
Hydrocolloid patches use a special gel layer to absorb fluid from pimples or wounds. These adhesive patches stick firmly to the skin. They form a protective barrier, shielding acne and minor cuts from bacteria and outside irritants.
The hydrocolloid gel reacts with liquid from pus or blisters, turning white as it absorbs moisture. This process helps reduce swelling and supports faster healing. Hydrocolloid dressings, gel patches, and wound patches all use this approach. Next, learn more in the material composition and fluid-absorbing properties overview.
Material composition and fluid-absorbing properties overview
- Hydrocolloid dressings combine carboxymethylcellulose, pectin, and gelatin to form a gel matrix that locks in fluid.
- Gel patches maintain an optimal moist environment on the skin, supporting natural wound healing processes.
- The colloid layer in hydrocolloid wound dressings swells as it absorbs pus and exudate from pimples or blisters.
- Hydrocolloid patches act as a hydrophilic barrier, preventing bacteria and irritants from reaching sensitive acne lesions.
Patch structure, gel formation, and wound healing performance
Hydrocolloid patches have multiple thin layers. The main hydrocolloid gel absorbs fluid from pimples or wounds. This gel layer creates a barrier against bacteria. Most gel patches and hydrocolloid dressings help skin heal faster by keeping the area moist and protected.
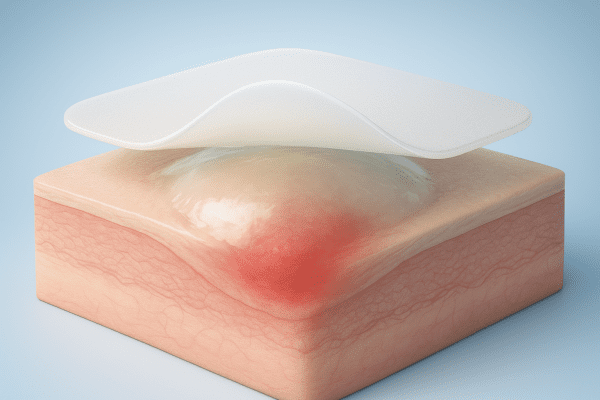
As the hydrocolloid gel reacts with pus or exudate, it swells and turns white. This process supports wound healing and reduces scarring risk. Colloid patches are gentle for different skin types and often used as wound care patches. Next, discover the details in layer design and gel-based healing mechanisms.
Layer design and gel-based healing mechanisms
- Multi-layer hydrocolloid dressings use a hydrocolloid gel core topped with a semi-permeable film to manage moisture and block bacteria.
- Gel patches trigger colloid formation upon contact with pus or exudate, helping support the skin’s natural healing process.
- Hydrophilic patches maintain a stable environment, reducing risk of scarring and protecting sensitive skin from external irritation.
- The adhesive layer in hydrocolloid wound patches securely seals the area, preventing fluid leakage and promoting effective wound care.
Managing pus, bacteria, and scarring with hydrocolloid patches
Hydrocolloid patches help manage pus and bacteria on pimples or wounds. These adhesive patches absorb fluid and shield skin from germs. By covering acne or minor cuts, hydrocolloid dressings can reduce scarring and promote healing. Many people choose these gel patches for easy, hygienic spot care.
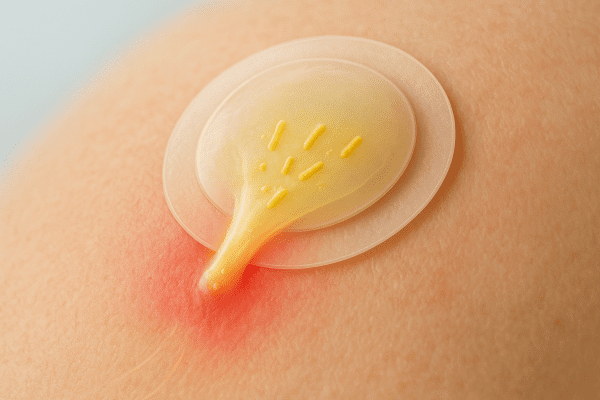
Colloid patches draw out pus and keep bacteria away from sensitive skin. They create a sealed barrier, which helps prevent picking and further scarring. Users often see reduced redness and faster healing. To understand how these hydrocolloid products control fluid and support scar prevention, learn more in the Role in fluid control and scar prevention section.
Role in fluid control and scar prevention
- Hydrocolloid dressings help trap exudate, reducing moisture loss from the skin and supporting the acne healing process.
- Gel patches create a sealed barrier that limits bacteria exposure and lowers the risk of new breakouts.
- Pimple patches minimize scarring by preventing direct contact with pimples and discouraging picking.
- Hydrophilic patches regulate fluid absorption, which helps keep the wound environment stable for skin recovery.
Skin types, patch application, and personal care routines
Hydrocolloid patches work on many skin types, including oily, dry, or sensitive skin. These adhesive patches fit into daily skin care routines. Pimple patches can help manage breakouts and minor wounds. Hydrocolloid gel patches are gentle and easy to use at home.
Proper patch application supports healing and reduces scarring risk. Each skin type may need special prep for best results. Hydrocolloid bandages remain affordable, usually $6–$18 per pack. Personal care routines with hydrocolloid dressings can be tailored for different needs. Learn more in the next section on Application steps for various skin types.
Application steps for various skin types
- Cleanse skin thoroughly before applying hydrocolloid patches to maximize adhesion and effectiveness.
- For oily skin, gently blot with a tissue to help adhesive patches stick securely and absorb pus.
- Sensitive skin types should patch test hydrocolloid gel patches on a small area to check for irritation.
- Apply hydrocolloid wound patches to dry skin and press firmly to create a hydrophilic seal over pimples or minor wounds.
Preventing picking, promoting healing, and reducing risk
Hydrocolloid patches create a barrier over pimples or wounds. This helps prevent picking and touching. The adhesive gel layer absorbs pus and protects skin. Using these hydrocolloid dressings supports natural healing and reduces the risk of infection or scarring.
Many consumers use hydrocolloid acne patches to avoid touching blemishes. These gel patches keep bacteria out and minimize irritation. Wound care patches help skin recover faster and reduce visible scars. Pricing for hydrocolloid products is typically $6–$18 per pack. Next, explore Behavioral benefits and risk reduction strategies for daily routines.
Behavioral benefits and risk reduction strategies
- Hydrocolloid patches encourage healthy skin-care habits by deterring the urge to touch or pick at pimples.
- Using adhesive patches lowers the chance of introducing bacteria to acne-prone skin.
- Gel patches support consistent acne treatment routines, making it easier to manage breakouts and scarring risk.
- Incorporating hydrocolloid dressings into daily personal care can reduce inflammation and promote better healing outcomes.
Hydrocolloid patch safety, irritation, and allergy precautions
Hydrocolloid patches are generally safe for most skin types. Some people may experience irritation or allergy. Always check the ingredient list before using adhesive patches or gel patches on sensitive skin. Hydrocolloid dressings should not be used on infected or deep wounds.

Rare side effects include redness, itchiness, or rash from colloid patches. If irritation occurs, remove the hydrocolloid patch and stop use. Hydrophilic patches are not recommended for those allergic to adhesives. For more details, see Common safety considerations and allergy guidance.
Common safety considerations and allergy guidance
- Always discontinue hydrocolloid patches if skin shows signs of allergy, such as redness or swelling.
- Patch test new hydrocolloid gel patches on a small area before regular use to check for irritation on sensitive skin.
- Avoid using hydrocolloid wound dressings over active infections or on broken skin to reduce risk of complications.
- Consult a dermatologist if reactions occur when using adhesive patches or hydrocolloid products with other acne treatments.
Comparing hydrocolloid dressings, gel patches, and wound care
Hydrocolloid dressings, gel patches, and wound care patches all help protect skin. Each uses a hydrocolloid layer to absorb fluid. These patch variations support healing for pimples, blisters, and minor wounds. Hydrocolloid patches are popular for both acne treatment and everyday wound care.
Gel patches are thin and flexible, ideal for acne spots. Hydrocolloid wound dressings handle more exudate and cover larger areas. Some hydrocolloid patches cost around $6–$18 per pack. Choosing the right patch depends on skin needs and area size. Next, see Differences in types and intended skin uses.
Differences in types and intended skin uses
- Hydrocolloid dressings are best for wound care on fingers or toes, while gel patches target acne and pimples on the face.
- Hydrocolloid film variations offer flexible coverage for blisters and minor cuts on active skin areas.
- Pimple patches are designed for spot acne treatment, absorbing pus and protecting sensitive skin from bacteria.
- Hydrophilic patches are often chosen for managing scarring and maintaining moisture in diverse skin-care routines.
Enhancing acne treatment with hydrocolloid and active ingredients
Hydrocolloid patches can be combined with active ingredients to boost acne treatment. These gel patches deliver targeted benefits for pimples, supporting faster healing. Many consumers use these hydrocolloid acne patches for whiteheads and minor breakouts.
Some hydrocolloid patch variations include entities like salicylic acid, tea tree oil, or niacinamide. These supplementary actives offer extra benefits for different skin types. Most hydrocolloid products with added actives cost around $8–$20 per pack. Next, learn about Supplementary ingredients and enhanced treatment effects.
Supplementary ingredients and enhanced treatment effects
- Some hydrocolloid gel patches deliver salicylic acid or niacinamide to target inflamed pimples and reduce redness.
- Incorporating active ingredients into hydrocolloid dressings can support faster skin recovery and boost acne treatment results.
- Colloid patches with added tea tree oil or exfoliants may help control bacteria and excess sebum on oily skin.
- Hydrocolloid wound care patches infused with supplementary agents can address both scarring and post-acne discoloration.
Long-term skin benefits and hydrocolloid patch maintenance
Hydrocolloid patches can help improve skin over time. Regular use of hydrocolloid dressings supports healing and reduces scarring. These gel patches create a barrier that protects skin from bacteria. Many users see clearer skin and fewer pimples with consistent use.
Proper maintenance of hydrocolloid patches is key for long-term results. Replace adhesive patches as directed, usually every 6–12 hours. Most hydrocolloid patch variations cost around $6–$18 per pack. Following good habits leads to lasting benefits and sets the stage for ongoing care and optimal usage practices.
Ongoing care and optimal usage practices
- Store hydrocolloid patches in a cool, dry place to preserve adhesive quality and gel performance.
- Dispose of used hydrocolloid bandages promptly to reduce bacteria exposure and maintain skin cleanliness.
- Alternate hydrocolloid gel patches with other skincare treatments, like retinoids or niacinamide, to support balanced acne care.
- Monitor skin for signs of irritation or allergy when integrating new hydrocolloid wound dressings into your personal care routine.
Final Thoughts:
Hydrocolloid patches offer an effective, convenient solution for managing acne and minor wounds, making them a staple in modern skincare routines. By creating a protective barrier and absorbing pus, these gel patches help reduce scarring and prevent bacteria from worsening breakouts. Whether you’re new to hydrocolloid acne patches or refining your acne treatment strategy, choosing the right patch for your skin type can significantly improve healing outcomes. Explore trusted brands or consult a dermatologist to find the best adhesive patches and optimize your personal care approach today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are hydrocolloid patches and how do they work for acne or minor wounds?1
Answer: Hydrocolloid patches are adhesive gel patches for skin. They absorb pus and fluid from pimples or wounds. The hydrocolloid layer forms a barrier. It protects the skin from bacteria and irritation. These patches help acne and wound healing. They are also called gel patches or hydrocolloid dressings.
How should hydrocolloid patches be applied for best results on different skin types?2
Answer: Clean and dry skin first. Apply the hydrocolloid patch to the pimple or wound. Press adhesive patches gently. For oily skin, blot before use. For sensitive skin, test the patch first. Hydrocolloid dressings, gel patches, and wound patches all follow these steps.
Can hydrocolloid patches help prevent scarring and reduce the urge to pick at pimples?3
Answer: Yes, hydrocolloid patches create a barrier over pimples. This discourages picking and touching the area. The colloid absorbs fluid and protects against bacteria. Regular use of gel patches can help reduce scarring. Wound care patches also support healthy skin recovery.
Are there any safety concerns or potential side effects associated with hydrocolloid patches?4
Answer: Hydrocolloid patches are safe for most skin types. Rarely, adhesive patches may cause irritation or redness. Sensitive skin can react to colloid or gel patches. Do not use hydrocolloid dressings on infected wounds. Discontinue use if allergy symptoms appear.
What is the difference between hydrocolloid patches, gel patches, and traditional wound dressings?5
Answer: Hydrocolloid patches and gel patches absorb pus from acne or wounds. Traditional wound dressings may not absorb fluid or form a gel. Hydrocolloid dressings seal and protect the skin. Hydrophilic patches are used for both acne and wound care. Each patch type targets different skin needs.
How long should hydrocolloid patches be worn, and how often can they be used?6
Answer: Wear hydrocolloid patches for 6–12 hours on pimples. For wound care, patches can stay up to 7 days. Replace adhesive patches when they turn white. Gel patches are safe for daily use. Always follow skin-care guidelines for hydrocolloid dressings.
Can hydrocolloid patches be used with other acne treatments or active skincare ingredients?7
Answer: Yes, hydrocolloid patches can be combined with some acne treatments. Use them after applying serums or creams. Wait for skin to dry before applying adhesive patches. Some gel patches contain active ingredients like salicylic acid. Check for interactions with other skincare products.
Who should avoid using hydrocolloid patches due to allergies or skin sensitivities?8
Answer: People allergic to adhesives or hydrocolloid materials should avoid these patches. Sensitive skin may react to gel patches or colloid. If redness, itchiness, or swelling appears, stop using hydrocolloid dressings. Consult a dermatologist before using hydrocolloid patches with known skin allergies.
Last Updated on January 28, 2026 by msj484
DISCLAIMER (IMPORTANT): This information (including all text, images, audio, or other formats on FamilyHype.com) is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional advice, diagnosis, endorsement or treatment. You should not take any action or avoid taking action without consulting a qualified professional. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions about medical conditions. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking advice or treatment because of something you have read here a FamilyHype.com.